The EU proposed a draft initiative imposing a ban on the use of Bisphenols A (BPA) in food contact materials (FCMs)
The EU proposed a draft initiative imposing a ban on the use of Bisphenols A (BPA) in food contact materials (FCMs)
On February 9, 2024, the European Union (EU) proposed a draft initiative imposing a ban on the use of bisphenol A (BPA) and certain other bisphenols in food contact materials (FCMs), including plastic and coated packaging. This follows the European Food Safety Authority’s publication, which indicates a concern for human health. Feedback can be sent to this website [1] before March 8, 2024.
Keynotes of the Proposal
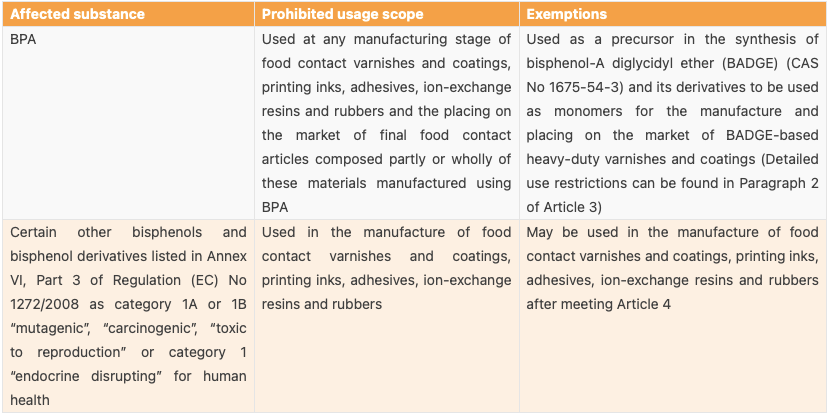
Based on EFSA’s opinion of 2023, the EU proposed to ban the use of BPA in FCM. As per the proposed draft, not only 4,4'-isopropylidene diphenol (BPA) (CAS No 80-05-7) but also some certain other bisphenols and bisphenol derivatives listed in Annex VI, Part 3 of Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 are prohibited to be used in FCMs, except for some circumstances. This is because these bisphenols and their derivatives may also present risks similar to BPA due to the similarities in their chemical structure and activity.
Table 1: Prohibited Usage Scope of BPA and Certain Other Bisphenols as well as the Exemptions
For enterprises, manufacturers placing the following FCMs on the market shall monitor the presence of BPA and its migration from a) materials and articles on which BADGE-based heavy-duty varnishes and coatings are applied; b) polysulfone resins for use in filtration membranes; and c) paper and board materials and articles containing recycled material. Business operators shall ensure the involved materials and articles are accompanied by a written declaration at all stages of marketing. The declaration of compliance shall contain the following information:
-
the identity and address of the business operator issuing the declaration of compliance;
-
the identity and address of the business operator that manufactures or imports the material or article;
-
the identity of the intermediate food contact material or the final food contact article;
-
the date of declaration;
-
confirmation that the intermediate food contact material or article or the final food contact article complies with the restrictions laid down in this Regulation and the requirements set out in Articles 3, 15, and 17 of Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004.
Moreover, corresponding regulations like Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 and Regulation (EC) No 1895/2005 are to be amended accordingly. Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 is to delete BPA (CAS No 80-05-7) from authorized substances and permit the use of “disodium 4,4'-Isopropylidene diphenolate” (CAS No 2444-90-8) only in the manufacture of polysulfone resins for use in filtration membranes. Regarding the revision of Commission Regulation (EC) No 1895/2005, the Draft revised the current provision “the use and/or presence of BFDGE in the manufacture of materials and articles are prohibited” as below.

To avoid production disruption, transitional provisions for different situations are expounded in Article 10. For example, single-use final food contact articles intended to be filled with processed fruits, vegetables, and fish products have a transitional period of 36 months, while many others are with a grace period of 18 months.
- [1] EU's initiative: restrictions on bisphenol A (BPA) and other bisphenols in food contact materials
- [2] EFSA's scientific opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs, 2015
- [3] EFSA's re-evaluation of the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs, 2023
- [4] EEA's briefing: Human exposure to Bisphenol A in Europe
- [5] EU Food Contact Materials Regulation
- [6] Sustainability.chemlinked.com





